Introduction
Indonesia, known for its stunning landscapes and vibrant culture, has emerged as a powerhouse in the global coffee industry. With its fertile soil, favorable climate, and rich coffee heritage, the country has become a significant player in coffee production and is renowned for its diverse coffee varieties. Indonesian coffee holds a special place in the hearts of both locals and coffee enthusiasts worldwide, making it a captivating subject to explore.
The Indonesian coffee industry is not just a source of economic prosperity but also deeply ingrained in the cultural fabric of the nation. Coffee has become an integral part of Indonesian daily life, enjoyed as a social beverage and symbolizing hospitality and warmth. This article aims to delve into the fascinating world of the Indonesian coffee industry, highlighting its historical background, unique coffee varieties, production process, role of smallholder farmers, coffee culture, export market, challenges, and future prospects
By understanding the nuances and significance of the Indonesian coffee industry, we can appreciate the efforts of those involved and gain insight into the factors contributing to its growth and success. So, join us as we embark on a journey to explore the captivating world of Indonesian coffee.
1. Historical Background
The history of coffee cultivation in Indonesia dates back to the 17th century when the Dutch colonialists introduced coffee plants to the archipelago. These plants found a favorable home in the volcanic soils of Indonesia’s islands, resulting in the establishment of coffee plantations across the country.

Dutch East India Company played a crucial role in the development of the Indonesian coffee industry, particularly in regions such as Java and Sumatra. Coffee quickly became a significant cash crop, driving economic growth and transforming Indonesia into one of the world’s leading coffee producers.
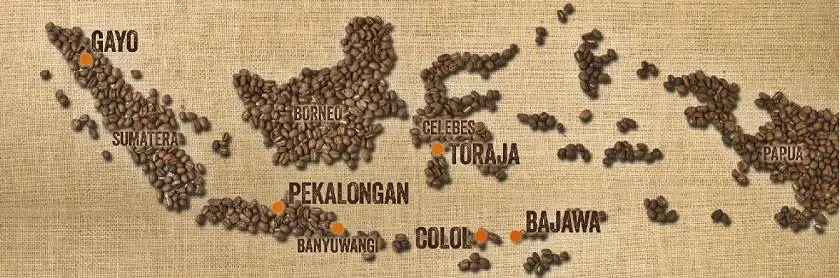
Over time, distinct coffee varieties emerged from different regions of Indonesia. Sumatran coffee, known for its full-bodied and earthy flavors, gained global recognition. Javanese coffee, with its mild and balanced taste, also became sought after. Other notable varieties include Sulawesi coffee, characterized by its richness and complexity, and Bali coffee, celebrated for its unique sweetness.
The influence of coffee on the Indonesian economy cannot be overstated. It played a pivotal role in shaping the country’s agricultural landscape and provided employment opportunities for numerous individuals. Moreover, coffee became deeply embedded in Indonesian culture, with coffee houses serving as social hubs and places for intellectual discussions.
Today, the rich historical legacy of the Indonesian coffee industry continues to thrive, as the country produces a diverse range of high-quality coffee beans coveted by coffee connoisseurs worldwide.
2. Coffee Varieties in Indonesia
Indonesia is renowned for its diverse coffee varieties, each with its own unique characteristics and flavors. Here are some of the notable coffee varieties grown in Indonesia:
a. Sumatran Coffee
Sumatra is home to one of the most famous Indonesian coffee varieties. Known for its full-bodied and earthy flavor profile, Sumatran coffee often exhibits notes of chocolate, herbs, and a hint of spice. The wet-hulling method, known as “Giling Basah,” used in processing Sumatra coffee, contributes to its distinct flavor profile.
b. Javanese Coffee
Coffee cultivation in Java dates back to the early 18th century. Javanese coffee is celebrated for its mild and balanced taste, often showcasing notes of nuts, fruits, and a subtle acidity. The volcanic soil and favorable climate contribute to the unique flavor profile of Java coffee.
c. Sulawesi Coffee
Grown on the highlands of Sulawesi island, this coffee variety is known for its richness and complexity. Sulawesi coffee exhibits a full body, low acidity, and a spectrum of flavors, including chocolate, nuts, and hints of exotic spices. The island’s unique microclimate and careful processing techniques contribute to the exceptional quality of Sulawesi coffee.
d. Bali Coffee
Bali’s coffee industry is relatively small but renowned for its unique sweetness. Bali coffee features a smooth and delicate flavor profile with subtle acidity. The volcanic soil of the island contributes to the coffee’s distinct characteristics, and the traditional “subak abian” irrigation system used in cultivation adds to its cultural significance.
Other coffee varieties grown in Indonesia include Aceh Gayo, Toraja, Flores, and Papua Wamena. Each variety offers a distinct experience, reflecting the diverse terroir and meticulous cultivation practices found across the Indonesian archipelago.
These Indonesian coffee varieties have gained recognition and admiration among coffee enthusiasts worldwide, contributing to the country’s reputation as a producer of exceptional specialty coffees.
3. Coffee Production Process
The production of Indonesian coffee involves several essential steps, from planting to harvesting and processing. Here’s an overview of the coffee production process in Indonesia:
a. Planting and Cultivation
Coffee plants thrive in the diverse microclimates and volcanic soils of Indonesia. Farmers carefully select suitable locations and plant coffee seeds or seedlings. The plants require ample shade, consistent rainfall, and well-drained soil for optimal growth.
b. Harvesting
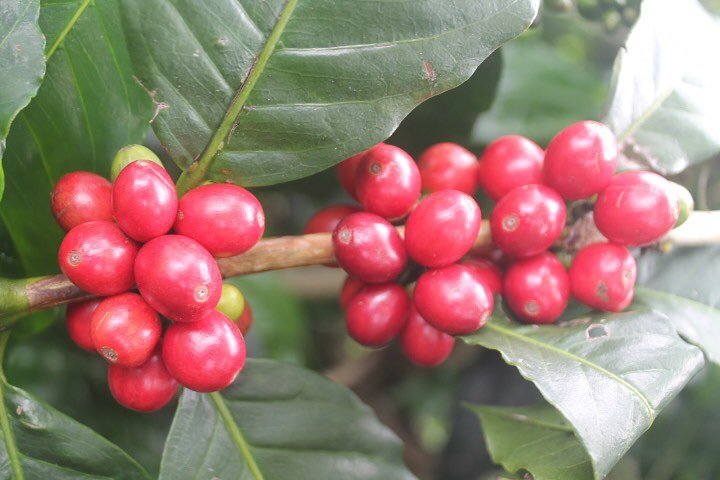
Coffee cherries ripen at different times depending on the variety and region. Skilled farmers selectively handpick the ripe cherries, ensuring only the highest quality ones are harvested. This meticulous process often involves multiple passes through the coffee fields to collect cherries at their peak ripeness.

c. Processing
Indonesia is known for employing unique processing methods that contribute to the distinct flavors of its coffees. One notable method is the “wet-hulling” or “Giling Basah” technique used for Sumatran coffee. This method involves removing the cherry’s skin and pulp, partially drying the beans, and then removing the parchment layer. The beans are then further dried to the desired moisture content. Other processing methods, such as fully washed and natural, are also employed depending on the coffee variety and farmer preferences.

Read also: Indonesia’s Specialty Coffee Processing: Unveiling the Science and Craftsmanship
d. Roasting
After the coffee beans are processed and dried, they are typically transported to roasters. Roasting is a critical step that determines the final flavor profile of the coffee. Indonesian coffee is often roasted to highlight its unique characteristics, with medium to dark roasts commonly preferred to bring out the inherent richness and complexity.

Read also: From Green to Brown: The Fascinating Process of Coffee Roasting!
e. Packaging and Distribution
Once the coffee beans are roasted, they are packaged and prepared for distribution. Local farmers may sell their coffee directly to consumers or supply coffee shops and local markets. Export-grade Indonesian coffee is carefully packaged and shipped to various international destinations, where it is enjoyed by coffee lovers around the globe.

Read also: Keep it Fresh: The Ultimate Guide to Coffee Beans Packaging
Sustainability and fair trade practices are increasingly important in the Indonesian coffee industry. Efforts are being made to promote environmentally friendly cultivation methods, support smallholder farmers, and ensure fair wages throughout the supply chain.
4. Role of Smallholder Farmers
The Indonesian coffee industry owes much of its success to the dedication and hard work of smallholder farmers. These farmers play a vital role in preserving traditional cultivation practices and maintaining the country’s rich coffee heritage. Here are some key points regarding the role of smallholder farmers in the Indonesian coffee industry:
a. Traditional Cultivation Practices
Smallholder farmers often follow age-old techniques passed down through generations, emphasizing organic methods and sustainable farming practices. They prioritize preserving the natural ecosystem, using minimal chemical inputs, and relying on the intercropping of coffee with shade trees to maintain biodiversity.
b. Coffee Heritage Preservation
Smallholder farmers are custodians of Indonesia’s coffee heritage. They cultivate local coffee varieties, safeguarding the unique flavors and characteristics that make Indonesian coffee distinct. By maintaining traditional cultivation methods, smallholder farmers contribute to the authenticity and cultural significance of Indonesian coffee.
c. Community Impact
Coffee farming is a source of livelihood for many rural communities in Indonesia. Smallholder farmers and their families are directly involved in the coffee production process, from planting and harvesting to processing and marketing. The income generated from coffee farming contributes to local economies, providing opportunities for education, healthcare, and infrastructure development.
d. Challenges Faced
Smallholder farmers face various challenges, including limited access to resources, fluctuations in coffee prices, and climate change impacts. Lack of financial capital, outdated equipment, and inadequate infrastructure hinder their ability to optimize production and reach wider markets. Initiatives focusing on capacity building, access to credit, and technical assistance can help address these challenges and support smallholder farmers.
e. Support and Empowerment
Several organizations, government initiatives, and fair trade movements are working to support and empower smallholder coffee farmers in Indonesia. These initiatives aim to provide training, improve access to markets, ensure fair prices, and promote sustainable farming practices. By empowering smallholder farmers, the Indonesian coffee industry can enhance its overall sustainability and contribute to rural development.
5. Indonesian Coffee Culture
Coffee holds a special place in Indonesian culture, with a rich coffee heritage and a vibrant coffee culture that spans generations. Here are some aspects of the Indonesian coffee culture worth exploring:
a. Traditional Coffee Preparation
Indonesian coffee culture often involves traditional brewing methods that have been passed down through generations. One such method is “kopi tubruk,” where finely ground coffee is mixed directly with hot water and left to settle before drinking. Another popular method is the “es kopi susu,” a sweet iced coffee mixed with condensed milk.

b. Coffee Houses and Social Hubs
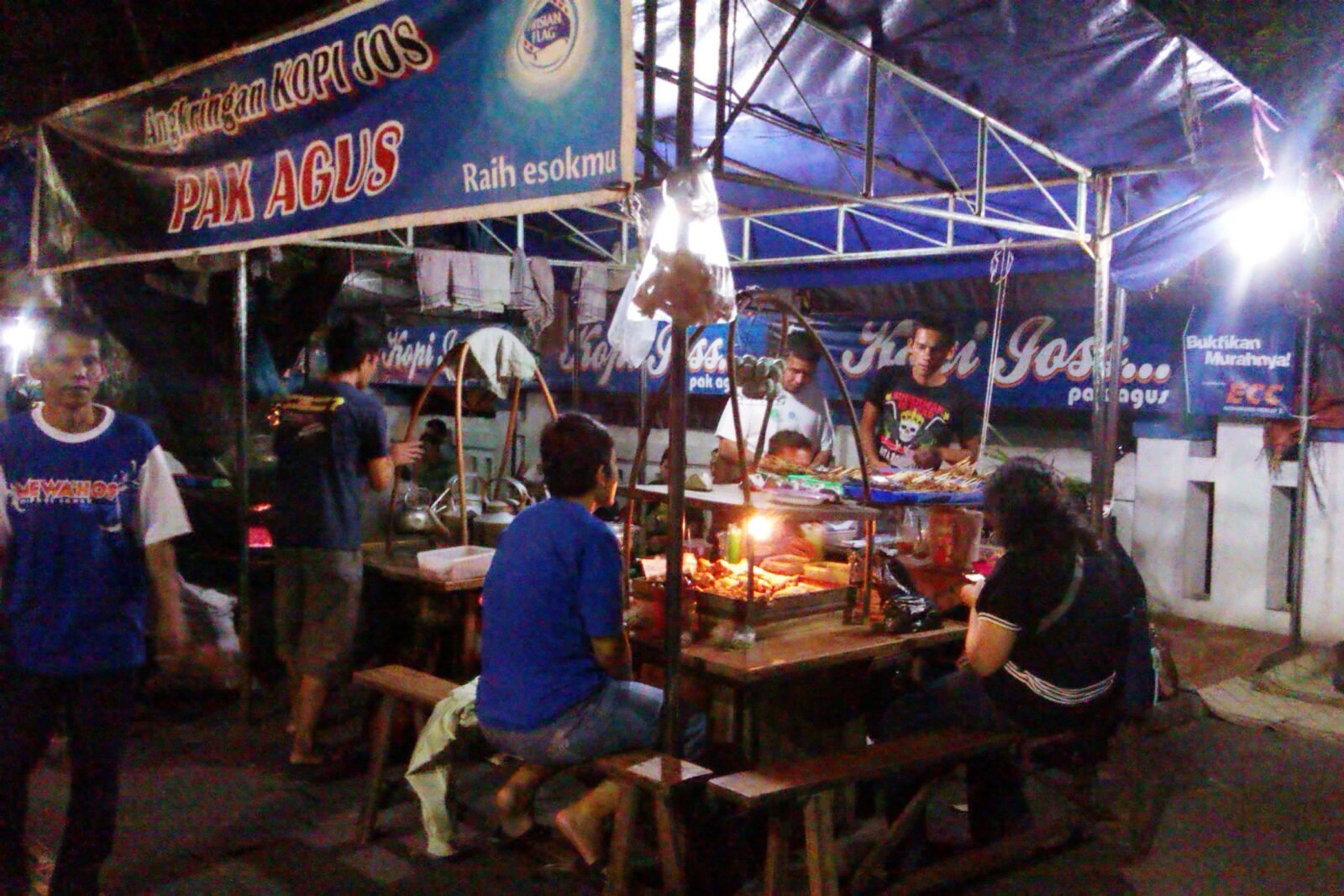
Coffee houses, locally known as “warung kopi” or “kedai kopi,” are integral to Indonesian coffee culture. These establishments serve as social hubs where people gather to enjoy a cup of coffee, engage in conversations, and discuss various topics ranging from politics to art and everyday life.

c. Specialty Coffee and Coffee Shops
Indonesian cities have witnessed a surge in specialty coffee shops that cater to coffee enthusiasts. These establishments focus on high-quality beans, precise brewing techniques, and offer a wide variety of coffee options from different regions of Indonesia. Specialty coffee shops provide a space for coffee lovers to explore and appreciate the nuances of Indonesian coffee.
d. Coffee-Related Traditions and Events
Indonesia boasts unique coffee-related traditions and events that showcase the country’s coffee culture. One such event is the Toraja Coffee Festival, held in the highlands of Sulawesi, where locals celebrate their coffee heritage through traditional ceremonies, coffee competitions, and cultural performances. Additionally, coffee cupping sessions, workshops, and latte art competitions are common in urban coffee events.
e. Coffee Tourism
The allure of Indonesian coffee has led to the rise of coffee tourism. Travelers from around the world visit coffee plantations, participate in coffee tasting sessions, and learn about the coffee production process firsthand. Coffee tourism offers an immersive experience, allowing visitors to appreciate the beauty of coffee landscapes while discovering the flavors and stories behind Indonesian coffee.
Indonesian coffee culture continues to evolve, blending tradition with innovation. The vibrant coffee houses, specialty coffee shops, and unique coffee-related traditions make it a captivating aspect of Indonesian society. It’s an experience that not only satisfies the taste buds but also provides a glimpse into the cultural fabric of the country.
6. Export and Global Influence

The Indonesian coffee industry has gained significant recognition and has a notable presence in the global market. Here are some key points regarding the export market and the global influence of Indonesian coffee:
a. Export Market
Indonesia is one of the largest coffee producers and exporters globally. The country exports a substantial volume of coffee each year, contributing to its economic growth and international trade. Key export destinations include the United States, Japan, European countries, and emerging markets in Asia.
b. Growing Demand for Indonesian Coffee
Indonesian coffee’s unique flavors, diverse varieties, and cultural significance have attracted the attention of coffee enthusiasts worldwide. There is a growing demand for Indonesian specialty coffees, especially those with distinctive profiles like Sumatran and Javanese coffees. The specialty coffee movement has played a significant role in promoting and highlighting Indonesian coffee in the global market.
c. Quality and Specialty Coffee
Indonesian coffee’s reputation for high-quality beans has led to its inclusion in specialty coffee offerings globally. Specialty coffee shops and roasters showcase Indonesian coffees, emphasizing their unique flavors and profiles. This exposure has helped to further elevate the image of Indonesian coffee and expand its market reach.
d. Global Influence on Coffee Trends
Indonesian coffee has influenced global coffee trends in several ways. The unique processing methods used in Indonesia, such as wet-hulling, have inspired experimentation in other coffee-growing regions. The distinct flavors and profiles of Indonesian coffee varieties have influenced roasting techniques and flavor preferences among coffee professionals and enthusiasts worldwide.
e. Opportunities for Growth
The increasing global demand for specialty coffee presents opportunities for the Indonesian coffee industry to further expand its market reach. With a focus on quality, sustainability, and innovation, Indonesian coffee producers and exporters can tap into new markets, establish stronger international partnerships, and contribute to the growth of the global coffee industry.
7. Challenges and Future Outlook
While the Indonesian coffee industry has experienced significant growth and success, it also faces various challenges. Understanding these challenges and exploring future prospects is crucial for its continued development. Here are some key points to consider:
a. Climate Change Impact
Climate change poses a significant threat to the Indonesian coffee industry. Rising temperatures, unpredictable weather patterns, and increased pest and disease pressures can impact coffee yields and quality. Adapting to climate change through innovative agricultural practices, resilient coffee varieties, and sustainable farming techniques is vital for the industry’s future.
b. Market Competition
The global coffee market is highly competitive, with various coffee-producing countries vying for market share. Indonesian coffee must differentiate itself by highlighting its unique flavors, sustainable practices, and quality. Strengthening marketing efforts and creating awareness about Indonesian coffee’s distinctiveness can help the industry maintain its competitive edge.

The coffee market continues to thrive with a projected revenue of US$88.35bn in 2023, experiencing an annual growth rate of 4.61%. The United States leads in revenue generation, reaching US$11,000.00m. Considering the global population, per person revenues of US$11.50 are expected in 2023. Additionally, the coffee market is anticipated to witness a volume growth of 2.4% in 2024, with a projected volume of 6.78bn kg by 2028. On average, each person is expected to consume 0.80kg of coffee in 2023. (Source: statista)
c. Infrastructure and Technology
Upgrading infrastructure and embracing technology is essential for the Indonesian coffee industry’s advancement. Improvements in transportation, processing facilities, and access to electricity and water resources can enhance efficiency and quality throughout the supply chain. Embracing digital tools and innovations can also streamline operations and improve market access.
d. Sustainability and Fair Trade
Emphasizing sustainability and fair trade practices is crucial for the long-term viability of the Indonesian coffee industry. Supporting smallholder farmers, promoting environmentally friendly cultivation methods, and ensuring fair wages and working conditions are essential for creating a sustainable and ethical coffee sector.
Read also: Coffee and Environmental Sustainability: Nurturing the Bean and Protecting the Planet
e. Innovation and Value Addition
Exploring opportunities for innovation and value addition can help the Indonesian coffee industry thrive. Developing new coffee products, such as specialty blends or single-origin micro-lots, and investing in research and development can enhance the industry’s competitiveness and expand market opportunities.
Looking ahead, the future outlook for the Indonesian coffee industry is promising. With its rich coffee heritage, diverse coffee varieties, and growing global recognition, Indonesian coffee is well-positioned to continue its upward trajectory. By addressing challenges, embracing sustainability, and capitalizing on emerging trends, the industry can unlock new opportunities and contribute to the country’s economic growth and cultural heritage.
Conclusion
The Indonesian coffee industry embodies a rich tapestry of history, culture, and flavors that have captivated coffee lovers worldwide. From its humble beginnings under Dutch colonial influence to its current position as a major player in the global coffee market, Indonesian coffee has achieved remarkable growth and recognition.
The journey through the Indonesian coffee industry has revealed several key insights. The historical background showcases the deep roots of coffee cultivation in Indonesia and its transformative impact on the country’s economy and culture. The diverse coffee varieties, such as Sumatran, Javanese, Sulawesi, and Bali coffee, offer a unique sensory experience that sets Indonesian coffee apart.
Understanding the coffee production process sheds light on the meticulous care taken by smallholder farmers in planting, harvesting, and processing coffee beans. Their dedication to traditional cultivation practices and preservation of coffee heritage are commendable.
Moreover, the vibrant coffee culture in Indonesia, from traditional brewing methods to the rise of specialty coffee shops, reflects the significance of coffee as a social and cultural symbol. Indonesian coffee has made a mark on the global stage, with its export market, growing demand for specialty coffee, and influence on coffee trends.
However, the Indonesian coffee industry also faces challenges, including climate change impact, market competition, and the need for infrastructure and technology advancements. Overcoming these challenges requires sustainable practices, innovation, and investment in the industry’s future.
Looking ahead, the Indonesian coffee industry has immense potential for growth and further contributions to the global coffee landscape. By focusing on sustainability, fair trade, infrastructure development, and embracing innovation, Indonesian coffee can continue to flourish while preserving its cultural heritage.
As coffee enthusiasts, it is our responsibility to appreciate and support the Indonesian coffee industry. Whether savoring a cup of Sumatran coffee or exploring the flavors of Javanese or Sulawesi coffee, we can actively participate in promoting the unique qualities and ensuring the industry’s sustainability.
In conclusion, the Indonesian coffee industry represents a harmonious blend of tradition, quality, and cultural significance. Let us raise our cups to celebrate the journey and taste the rich flavors that Indonesian coffee has to offer.